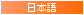
【石】 Seki / Ishi Stone
|
Until Shirakawa Kanji science became known, the 口 of 石 was traditionally explained as a piece of stone lying below a cliff. The tortoise plastron and bone characters, however, show that 口 is a sacred receptacle for putting in prayer writings. As was introduced in the explanation of 暦 ‘koyomi: calendar,’ 厂 shows the form of a steep cliff, and cliffs were regarded as places of strong spiritual power and were used for various religious services, worship and rituals. Other characters showing the relation between stones and spiritual power are 宕 and 祏. 宕, which shows a mausoleum, has 石 below 宀 a mausoleum roof. 祏, which means an ancestor tablet, combines the 示 altar classifier with 石. From 石 appearing in characters related to rituals and worship, it may be inferred that stones also functioned as altar.
Not only in antiquity, but also in the present, people with strong spiritual sense warn to take stones away from nature and bring them home as one pleases as spirits can easily dwell in these basic elements of nature. In Japan, especially in shrines, worship of stones can often be seen.
Not only in antiquity, but also in the present, people with strong spiritual sense warn to take stones away from nature and bring them home as one pleases as spirits can easily dwell in these basic elements of nature. In Japan, especially in shrines, worship of stones can often be seen.
- name
- Editoral supervision: Dr. Christoph Schmitz, Researcher of Shirakawa Kanji Science, General and Japanese History of Philosophy and Thought
- hp
- http://nippon-kichi.jp/article_list.do?p=5332