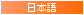
【卜】 Boku Divination, Auguration
|
This character is the form of a crack deliberately added on a tortoise plastron or animal bone in order to divine before the tortoise plastron and bone characters are inscribed. The backside of the tortoise plastrons or animal bones being the divination material is dug and made flat, creating a hole to which an iron stick is applied. The character form shows the figure of the crack appearing on the opposite side.
Among the variant forms of 卜, this form is regarded as lucky or auspicious. The traditional name of the vertical line is 千里 ‘senri: thousand Ri (1 Ri is 3.9 km)’ and the horizontal line is called 坼 ‘taku: split, crack.’ When the ‘taku’ line is crooked halfway, it gets the meaning of ill (bad) luck. 卜 also is one of the characters indicating that the luck – bad luck alternative is a central way of thinking in Oriental culture. Among the animal bones the shoulder blades of oxen, the horns and skulls of deer, the rips and others of female rhinoceroses and the skulls of prisoners of war were used. Regarding tortoise plastrons there are two, the belly plate and the carapace; 甲, the character of the belly shell or plastron shows the flat, square belly plate, the plastron. As the back shell or carapace was seldom inscribed, this can rarely be seen. As the back shell is round and very hard, it is quite difficult to dig a hole in it for producing a divination crack.
As in ‘Western’ Kanji research not the correct ‘tortoise plastron and bone writing,’ but generalized wording like ‘tortoise shell or carapace’ not naming the plastron is used for the translation of 甲骨文 ‘Kōkotsubun,’ the original form or correct image usually is not conveyed clearly. One reason for this is that the character 甲 which originally shows the tortoise plastron is mainly used in compounds like 甲羅 ‘Kōra: tortoise shell’ and 亀甲 ‘Kikkō: tortoise shell, carapace.
Among the variant forms of 卜, this form is regarded as lucky or auspicious. The traditional name of the vertical line is 千里 ‘senri: thousand Ri (1 Ri is 3.9 km)’ and the horizontal line is called 坼 ‘taku: split, crack.’ When the ‘taku’ line is crooked halfway, it gets the meaning of ill (bad) luck. 卜 also is one of the characters indicating that the luck – bad luck alternative is a central way of thinking in Oriental culture. Among the animal bones the shoulder blades of oxen, the horns and skulls of deer, the rips and others of female rhinoceroses and the skulls of prisoners of war were used. Regarding tortoise plastrons there are two, the belly plate and the carapace; 甲, the character of the belly shell or plastron shows the flat, square belly plate, the plastron. As the back shell or carapace was seldom inscribed, this can rarely be seen. As the back shell is round and very hard, it is quite difficult to dig a hole in it for producing a divination crack.
As in ‘Western’ Kanji research not the correct ‘tortoise plastron and bone writing,’ but generalized wording like ‘tortoise shell or carapace’ not naming the plastron is used for the translation of 甲骨文 ‘Kōkotsubun,’ the original form or correct image usually is not conveyed clearly. One reason for this is that the character 甲 which originally shows the tortoise plastron is mainly used in compounds like 甲羅 ‘Kōra: tortoise shell’ and 亀甲 ‘Kikkō: tortoise shell, carapace.
- name
- Editoral supervision: Dr. Christoph Schmitz, Researcher of Shirakawa Kanji Science, General and Japanese History of Philosophy and Thought
- hp
- http://nippon-kichi.jp/article_list.do?p=5332